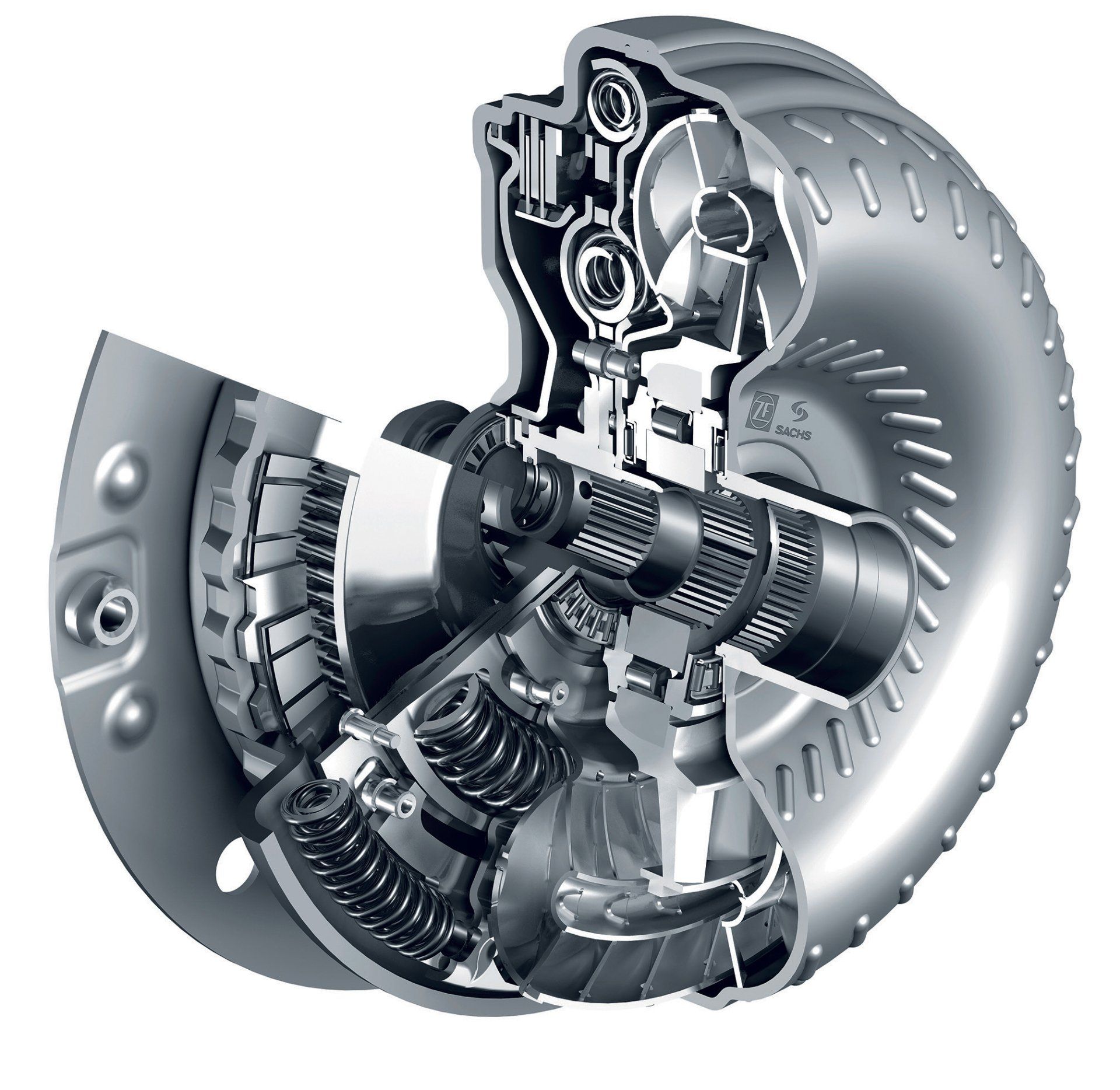
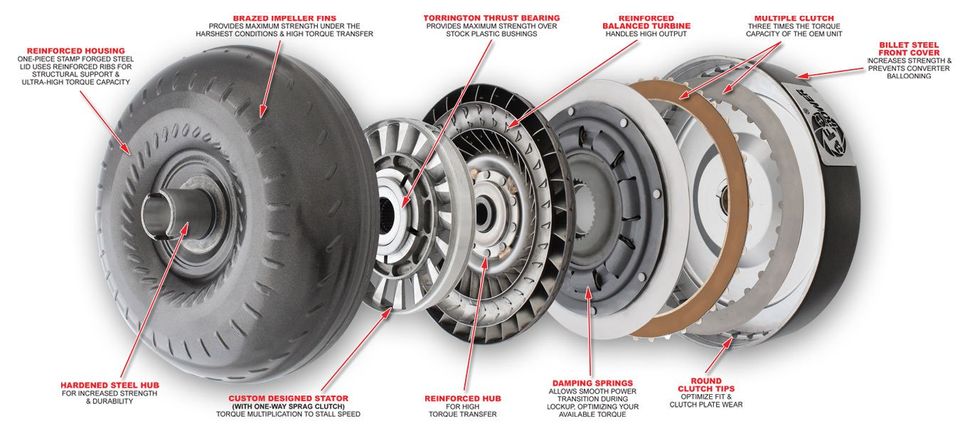
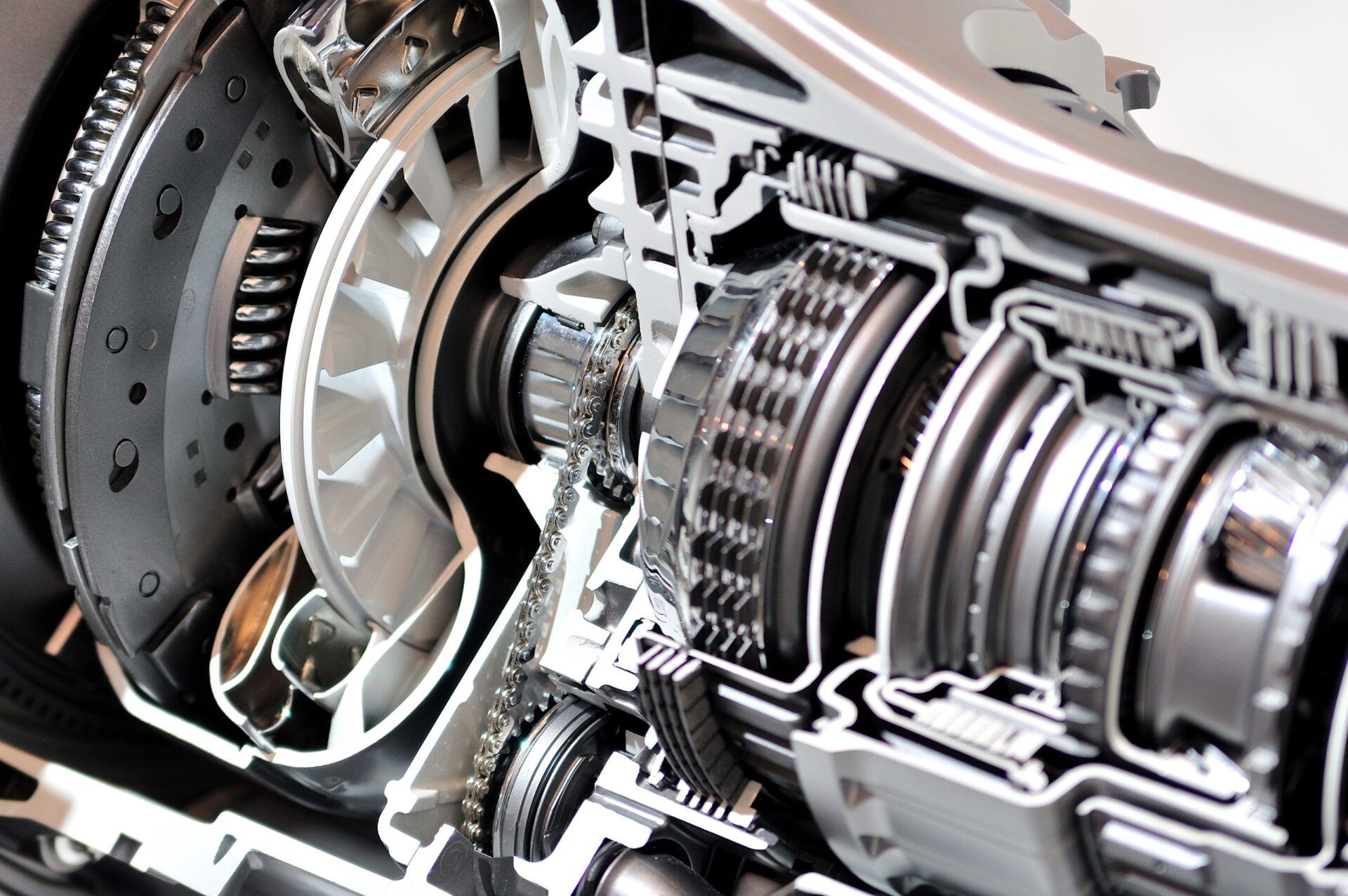
It's a doughnut-shaped internal engine component directly attached between the engine and transmission. Inside the torque converter, there are two series of curved blades, each facing the opposite direction.
The space inside of it is normally full of transmission fluid, which helps in transferring power generated from the engine to the transmission. It seems odd, right? Not really! Your vehicle’s engine drives one of the turbines also known as the impeller, that pushes the fluid onto the turbine.
The torque converter is efficient since its blades are precisely engineered to maximize the energy transmission reducing heat buildup or turbulence.
A better way to understand its working is to imagine two fans facing each other. When a single fan plugs into the mains (the engine), it will begin to move the second fan (transmission).
In case the fan blades are of the same dimension and weight, they will spin at the same rate. However, this is a rough simplification of how the torque converter works.
There are a few factors that make it possible for the torque converter to be more efficient; this includes the stator, which helps it redirect the flow of transmission fluid back to the impeller for improved efficiency.